Plant-Based Meat
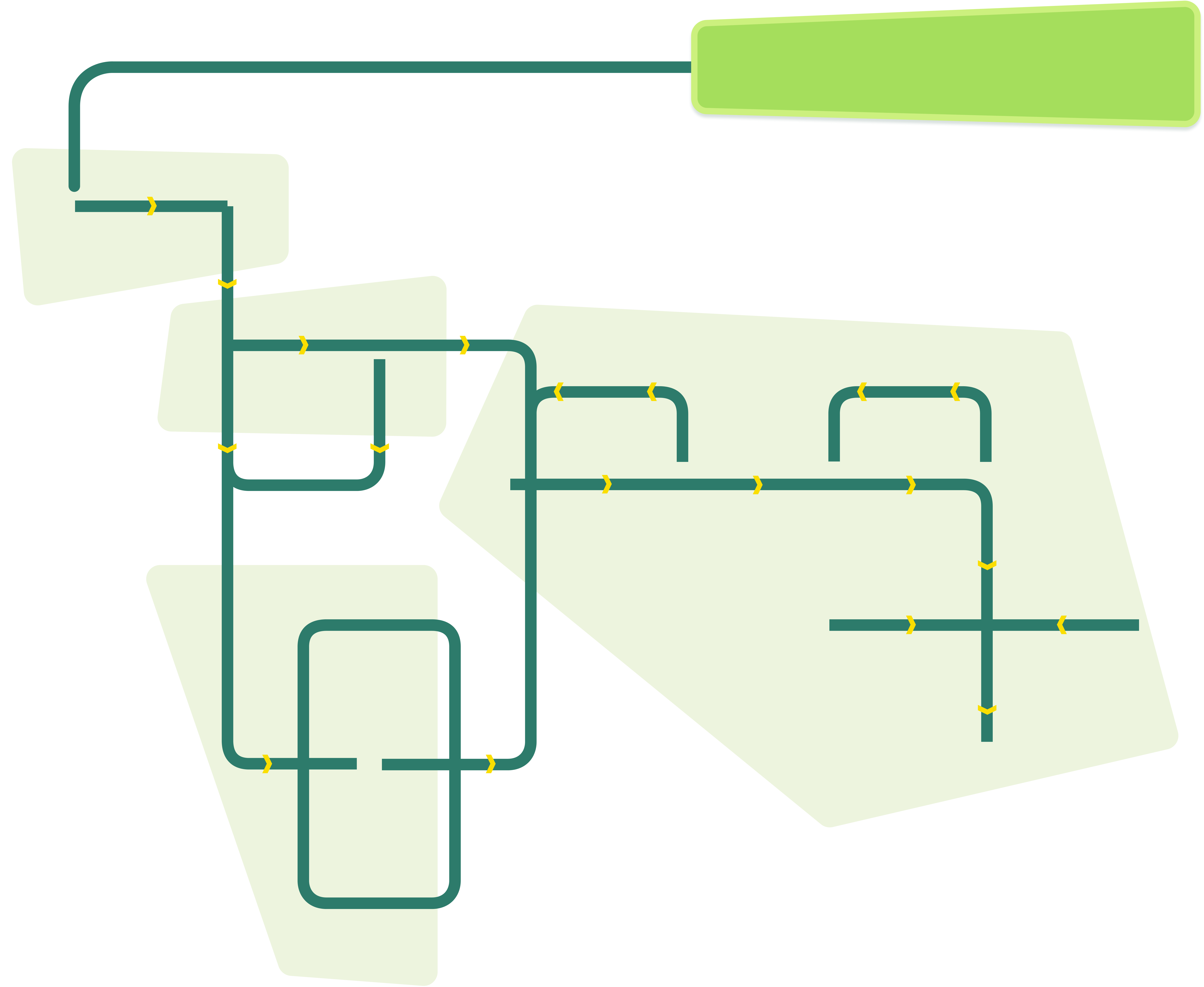
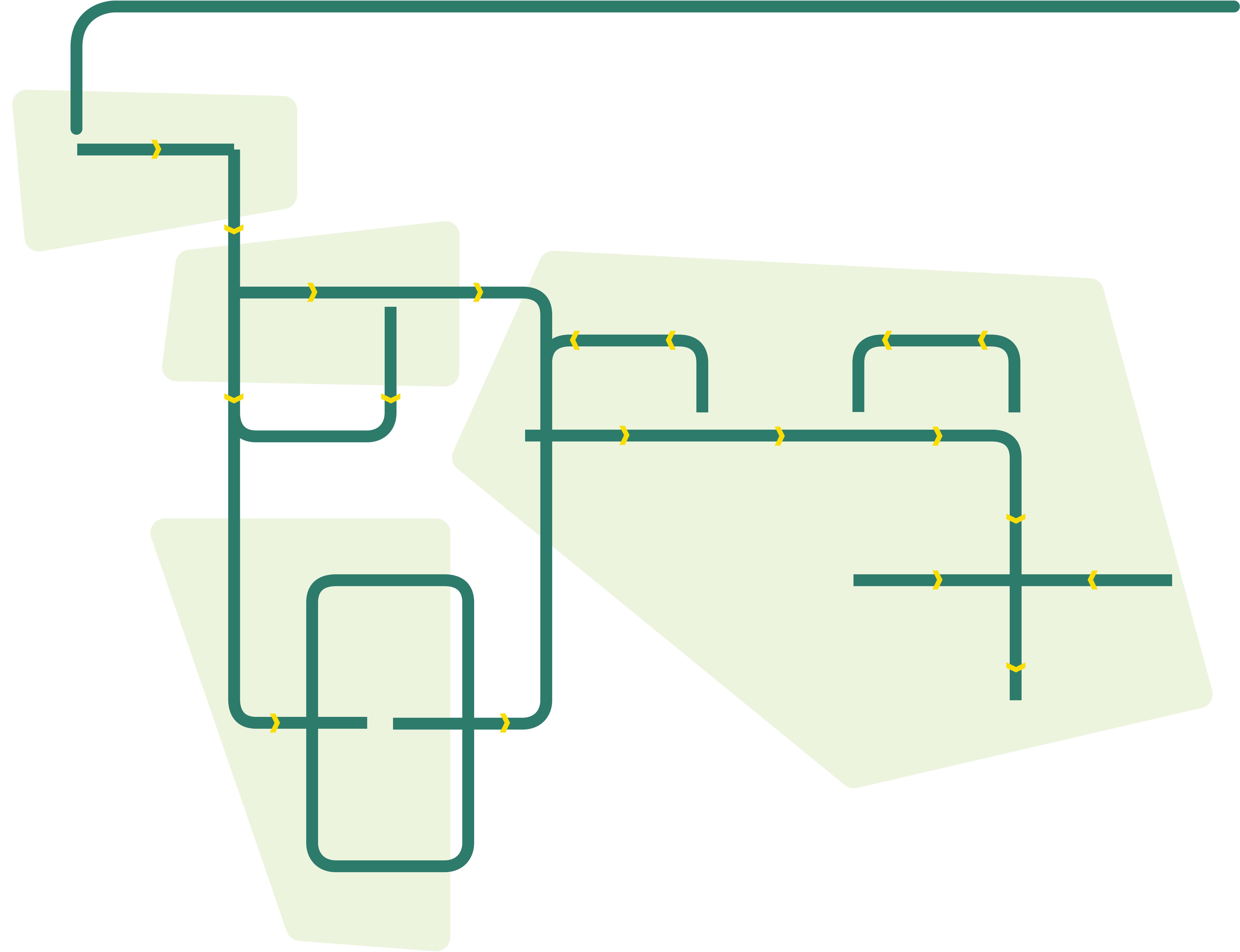
This page provides a comprehensive overview of the plant-based meat (PBM) value chain map. It aims to help users understand the workflow involved in plant-based meat production, discusses the various jobs required at each stage, identifies the necessary skills for these roles, and offers guidance on where to acquire such skills. Whether you are a student, a professional looking to transition into the industry, or simply curious about the process, this page will serve as an informative resource.








What is Plant-Based Meat?
PBM is an innovative alternative to conventional meat products, designed to mimic the taste, texture, and nutritional profile of animal meat using plant-derived ingredients. PBM products are created using a variety of plant proteins, such as soy, peas, and wheat, which are processed and combined with other natural ingredients to replicate the sensory experience of eating animal meat. Advances in food science and technology have enabled the development of plant-based meats that closely resemble their animal counterparts, appealing to both vegetarians and meat-eaters alike.
Why Talent is Needed
The PBM industry is growing rapidly, driven by increasing consumer demand for secure and sustainable food options. To continue this growth and innovation, the industry needs talented professionals from various fields, including food science, nutrition, culinary arts, agricultural science, and food engineering. Experts in plant protein extraction and processing, flavour development, and food texture engineering are particularly crucial to improving the quality and appeal of PBM products. Additionally, marketing, regulatory compliance, and supply chain management are essential to bring these innovative products to market. As the industry evolves, the collaboration of diverse skill sets and expertise will be necessary to overcome technical challenges and meet the evolving preferences of consumers.
Your Impact
Working in the plant-based meat industry offers the chance to make a meaningful impact on both global health and the environment. Producing PBM requires significantly fewer resources than conventional animal farming, leading to a dramatic reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land consumption. This shift can contribute to combating climate change and preserving natural ecosystems. On a health level, PBM can offer lower saturated fat and cholesterol compared to animal meat, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases. By providing a delicious alternative to conventional meat, professionals in this field are helping to build a more sustainable, healthy, and secure food system for future generations.