Cultivated Meat
This page provides a detailed overview of the cultivated meat value chain map. It aims to help users understand the workflow involved in producing cultivated meat, discusses the various jobs required at each stage, identifies the necessary skills for these roles, and offers guidance on where to acquire these skills. Whether you are a student, a professional looking to transition into the industry, or simply curious about the process, this page will help guide you in the right direction.




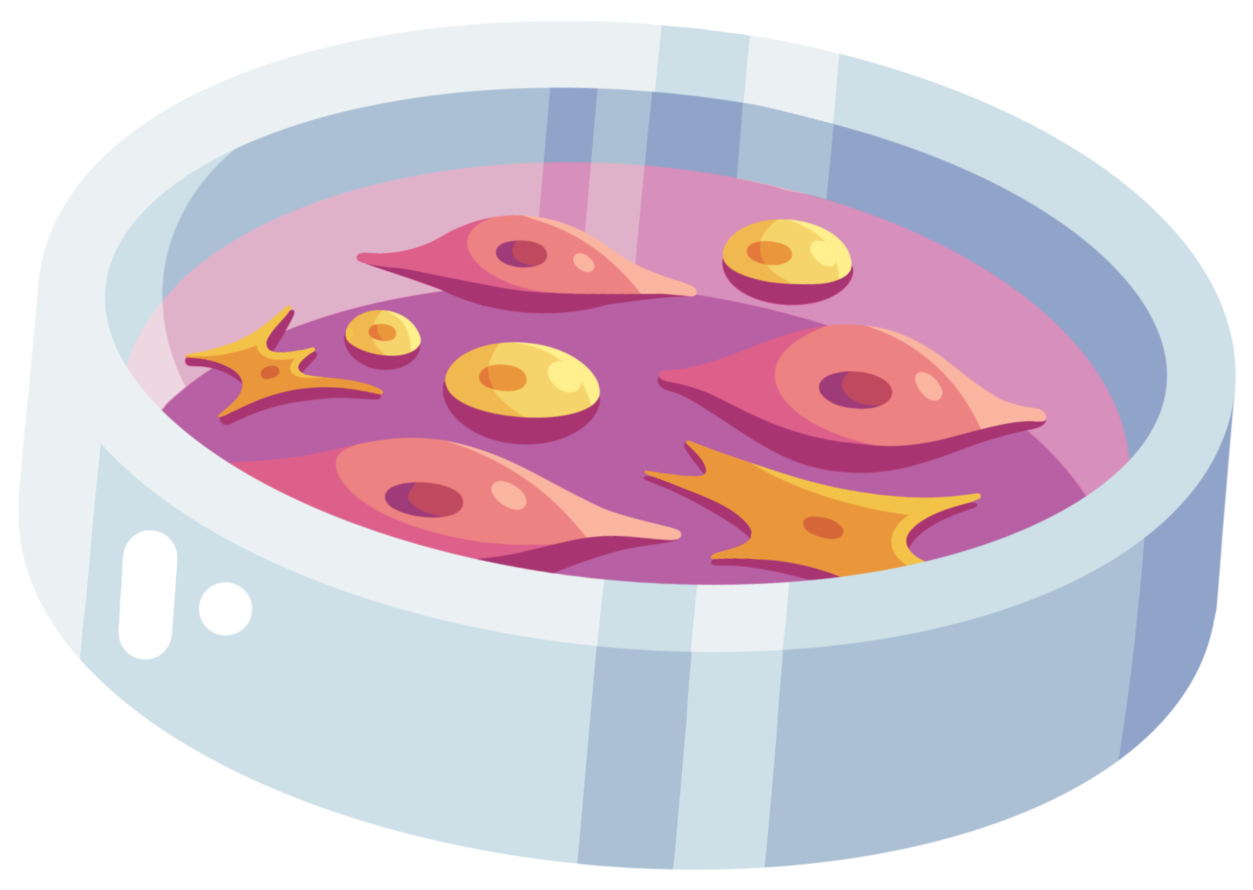
What is Cultivated Meat?
Cultivated meat is genuine animal meat cultivated directly from cells in a controlled environment. The production process begins by sourcing animal cells through a minimally invasive biopsy. These cells are then cultured in a nutrient-rich medium, enabling them to proliferate and differentiate into muscle tissue, fat, and other components that make up conventional meat. Cultivated meat is made of the same cell types arranged in the same or similar structure as animal tissues, thus replicating the sensory and nutritional profiles of conventional meat. This technology holds the promise of providing meat without the associated drawbacks of conventional animal agriculture, such as environmental degradation, zoonotic disease risks, and resource inefficiencies.
Why Talent is Needed
The cultivated meat industry is rapidly evolving and requires a diverse talent pool to drive innovation and bring products to market. Professionals from various disciplines, including bioprocess engineering, molecular biology, tissue engineering, food science, and regulatory affairs, are essential to overcoming the technical and logistical challenges involved. Expertise in cell culture, bioreactor design, scaling up production processes, and ensuring food safety and quality are critical for the industry’s success. Additionally, interdisciplinary collaboration is vital to integrate advancements from biotechnology, material science, and food technology. The need for skilled individuals is paramount as the industry scales from R&D to commercial production, to ensure that cultivated meat products are safe, affordable, and accessible to consumers.
Your Impact
Working in the cultivated meat industry offers a unique opportunity to make a significant, positive impact on the world. Cultivated meat production has the potential to drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption compared to conventional livestock farming. By eliminating the need for raising and slaughtering animals, this technology can also improve animal welfare and reduce the spread of zoonotic diseases. Furthermore, it can contribute to global food security by providing a sustainable source of protein for our growing human population. Professionals in this field are not only advancing scientific and technological frontiers but also contributing to a more sustainable and secure food system.

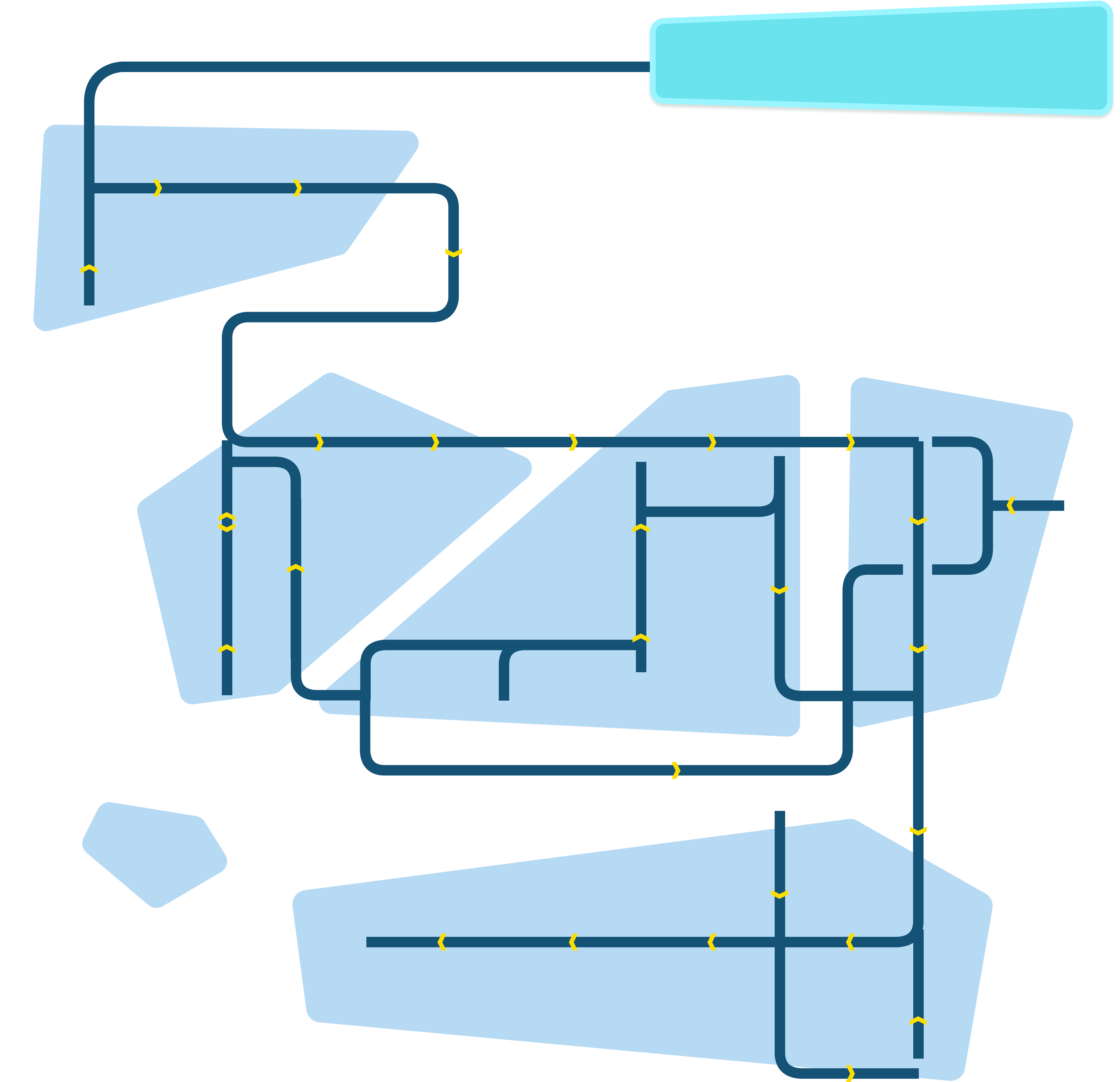
Value Chain Map
Value Chain Map
The technology value chain map outlines the step-by-step process of cultivated meat production. Users can click on each bubble to learn more about the workflow, equipment used, and job archetypes associated with that step of the value chain. The map is divided into key stages of development, making it easier to follow the flow of work that brings cultivated meat from cell isolation to market-ready products.

Biopsy or Tissue Sourcing

Cell Isolation & Purification

Cell Culture Establishment

Donor Animal Selection
Cell Line Development & Optimisation
Quality Assurance/Quality Control & Safety
Cell Banking

Seed Train Expansion

Primary Bioreactor Proliferation

Secondary Bioreactor Inoculation

Bioprocess Optimisation

Culture Media Dev & Optimisation
Supply Chain Optimisation

Scaffold Development

Automation & Intensification

In Silico Modelling

Bioprocess Optimisation
Differentiation & Maturation

Harvest

Food Formulation
Sensory Analysis & Product Optimisation

Quality Assurance/ Quality Control

Post-Processing: Texturing & Flavouring

End Product Packaging & Labelling

Manufacturing

Final Product Sales
Regulatory Affairs





The technology value chain map outlines the step-by-step process involved in cultivated meat production. Users can click on each step to learn more about the specific activities, equipment used, and jobs associated with that stage. The map is divided into key stages of development, making it easier to follow the flow of work and understand the intricate processes that bring cultivated meat from cell isolation to market-ready products.
Job Archetype Map
This section explores the various job archetypes within the cultivated meat industry. It provides detailed descriptions of each role, highlights their responsibilities, the skills required, and the typical backgrounds that are a good fit. Additionally, it offers insights on where to bridge any skill gaps, making it a valuable resource for those looking to enter or advance within the industry.